Canonical tags are a critical yet often overlooked part of technical SEO. When used correctly, they help prevent duplicate content issues, consolidate page authority, and ensure Google indexes the correct version of your web pages.
If you’re not using canonical tags properly, you could be losing rankings and traffic due to content duplication. This guide explains what canonical tags are, why they matter, and how to implement them correctly in 2025.
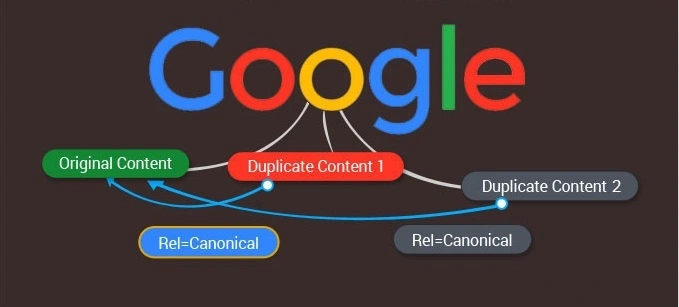
1. What Are Canonical Tags?
A canonical tag (rel="canonical") is an HTML element that tells search engines which version of a page is the “preferred” one. It helps Google understand which page to rank and index, preventing duplicate content issues.
Example of a Canonical Tag:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-page/" />This tells Google that https://example.com/preferred-page/ is the main version of the content.
2. Why Are Canonical Tags Important for SEO?
1. Prevents Duplicate Content Issues
Google penalizes duplicate content because it confuses search engines and dilutes rankings. Canonical tags tell Google which page to prioritize.
2. Consolidates Page Authority
If multiple URLs contain similar content, canonical tags consolidate link equity to the main page, preventing keyword cannibalization.
3. Improves Crawl Efficiency
Canonicalization ensures that search engines don’t waste crawl budget on duplicate pages, allowing them to focus on indexing valuable content.
4. Helps E-commerce & Dynamic Websites
Online stores often have multiple versions of a product page (due to filters, tracking parameters, etc.). Canonical tags help Google understand which version to index.
3. How to Set Up Canonical Tags Correctly
1. Implement Canonical Tags in the <head> Section
Every duplicate or similar page should have a canonical tag pointing to the original version.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/original-page/" />2. Use Self-Referencing Canonical Tags
Even the main version of the page should have a self-referencing canonical tag to avoid accidental duplication.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/this-page/" />3. Canonicalize HTTP to HTTPS Versions
If your site has both HTTP and HTTPS versions, ensure your canonical tag points to the secure HTTPS version.
4. Handle URL Parameters & UTM Tags Properly
Google treats URLs with parameters differently, so use canonical tags to prevent duplicate indexing.
✅ Good Practice:
https://example.com/shoes?color=red → Canonicalized to → https://example.com/shoes/5. Avoid Conflicting Signals (301 Redirects vs. Canonicals)
Don’t mix 301 redirects with canonical tags for the same URL—it confuses Google. Use 301 redirects for permanent removals and canonical tags for duplicate variations.
6. Use Canonical Tags on Paginated Content
For paginated pages (?page=2, ?page=3), use self-referencing canonicals instead of pointing all to page 1.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/blog?page=2" />4. Common Canonical Tag Mistakes to Avoid
🚨 Mistake 1: Pointing All Pages to the Homepage ➡ This confuses search engines and causes indexing issues. Only canonicalize pages with similar or duplicate content.
🚨 Mistake 2: Using Multiple Canonical Tags on One Page ➡ Having more than one <link rel="canonical"> tag creates conflicting signals and may cause Google to ignore them.
🚨 Mistake 3: Using Canonicals for Completely Different Content ➡ Canonicals should only be used for near-identical or duplicate pages. Misusing them can lead to de-indexing of valuable content.
🚨 Mistake 4: Forgetting to Update Canonical Tags After Site Migrations ➡ If you’ve migrated a website, ensure all canonical tags point to the new domain to maintain rankings.
🚨 Mistake 5: Not Checking Google Search Console for Errors ➡ Regularly check Google Search Console > Indexing > Pages for canonicalization issues.
5. How CG Marketing Can Help Fix Your Canonical Tag Issues
At CG Marketing, we provide expert technical SEO solutions to ensure your website is properly indexed and free from duplicate content issues.
✅ SEO Services: Technical SEO audits, canonical tag implementation, and indexing fixes.
✅ Web Development: Optimized website structures with correct canonicalization.
✅ Social Media Marketing: AI-enhanced content strategies to drive traffic.
✅ UI/UX Design: Fast-loading, SEO-friendly websites.
✅ Paid Advertising: Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and advanced PPC campaigns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What happens if I don’t use canonical tags?
Without canonical tags, Google might index duplicate content, causing ranking dilution and keyword cannibalization.
2. How do I check if my canonical tags are working?
Use Google Search Console > URL Inspection Tool to see which version Google has indexed.
3. Should I use canonical tags or 301 redirects?
Use 301 redirects for permanently removed pages and canonical tags for duplicate variations that should remain accessible.
4. Can I use rel=”canonical” across different domains?
Yes, but Google treats cross-domain canonicals as hints, not directives. Use them carefully.
5. How often should I check my website for canonical errors?
Perform a technical SEO audit every 3-6 months to ensure all canonical tags are correctly implemented.
Final Thoughts: Master Canonical Tags for Better SEO in 2025
Canonical tags are a powerful tool to control duplicate content, consolidate SEO authority, and improve crawl efficiency.
✅ What to Remember:
✔ Use self-referencing canonical tags on original content.
✔ Canonicalize duplicate product pages and parameterized URLs.
✔ Avoid conflicting signals (301 redirects + canonicals).
✔ Regularly check Google Search Console for canonical issues.
🔍 Need help implementing canonical tags? Claim your FREE website audit today!
